Table of contents

Whether in manufacturing or other complex industries, delivering high-quality products is a cornerstone of business success. Quality management processes like Quality Assurance (QA) and Quality Control (QC) are pivotal in ensuring consistency, reliability, and customer satisfaction.
Yet, these terms are often misunderstood, leading to, confusion, inefficiencies, and missed opportunities for improvement.
The distinction between QA and QC is crucial for achieving such results. Understanding these differences is the foundation of better decision-making and operational efficiency for managers, supervisors, and directors.
This article will clarify the differences between QA and QC, explore how they work together, and offer actionable strategies for implementing both in your organization.
Why Quality Matters in Today’s Enterprises
Superior quality can be the difference maker that makes the final product stand out from your competitors in a highly competitive field.
Why is that? Well, high-quality products build customer trust, foster loyalty, and enhance brand reputation. Conversely, lapses in quality can lead to devastating consequences, such as regulatory fines, product recalls, or loss of market share.
Take the pharmaceutical manufacturing process as an example. Regulatory bodies like the FDA and EMA enforce stringent quality requirements to ensure public safety. Failing to meet these standards can result in costly recalls or legal actions.
Similarly, in the automotive industry, a single manufacturing defect can cascade into massive recalls and reputational damage. For instance, Takata’s recall for faulty airbags in millions of vehicles led to one of the most expensive recalls in history, costing the manufacturer billions of dollars and ultimately filing for bankruptcy. These cases underscore the critical importance of robust quality systems.
For industries like food and beverage, quality failures can have life-threatening consequences. Contaminated products not only harm consumers but also result in eroded trust and significant financial losses. Companies that excel in quality management, on the other hand, consistently exceed customer expectations while maintaining compliance with safety regulations.
Defining Quality Assurance (QA) and Quality Control (QC)
What is Quality Assurance?
Quality Assurance is a proactive and systematic approach to quality management. The primary goal of quality assurance is to design and implement processes that prevent defects from occurring in the first place. Unlike QC, which focuses on the end product, QA emphasizes process improvement and consistency throughout the production lifecycle.
For example, in food manufacturing, QA might involve developing comprehensive HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) plans to identify and mitigate risks at every stage of production. Similarly, in electronics manufacturing, QA could include setting design guidelines to ensure components meet performance and reliability standards before production begins.
Stuck with managing HACCP compliance? Access Certainty Software’s free-to-download HACCP Food Safety Checklist today.

30+ Audit and inspection checklists free for download.
What is Quality Control?
Quality Control, on the other hand, is reactive. It involves inspecting and testing products to identify and correct defects after they occur. QC serves as the final checkpoint, ensuring that only products meeting the required specifications reach the customer.
For instance, in automotive manufacturing, QC teams might inspect vehicles for paint defects, engine performance issues, or electrical malfunctions. These inspections are crucial for identifying problems that could lead to recalls or customer dissatisfaction.
While QC is essential for maintaining quality standards, it works best when paired with strong QA practices. Together, they form a comprehensive system for managing quality across all stages of product development.
Key Differences Between Quality Assurance and Quality Control
Understanding the differences between QA and QC is essential for optimizing your quality management strategy. Here’s a side-by-side comparison:
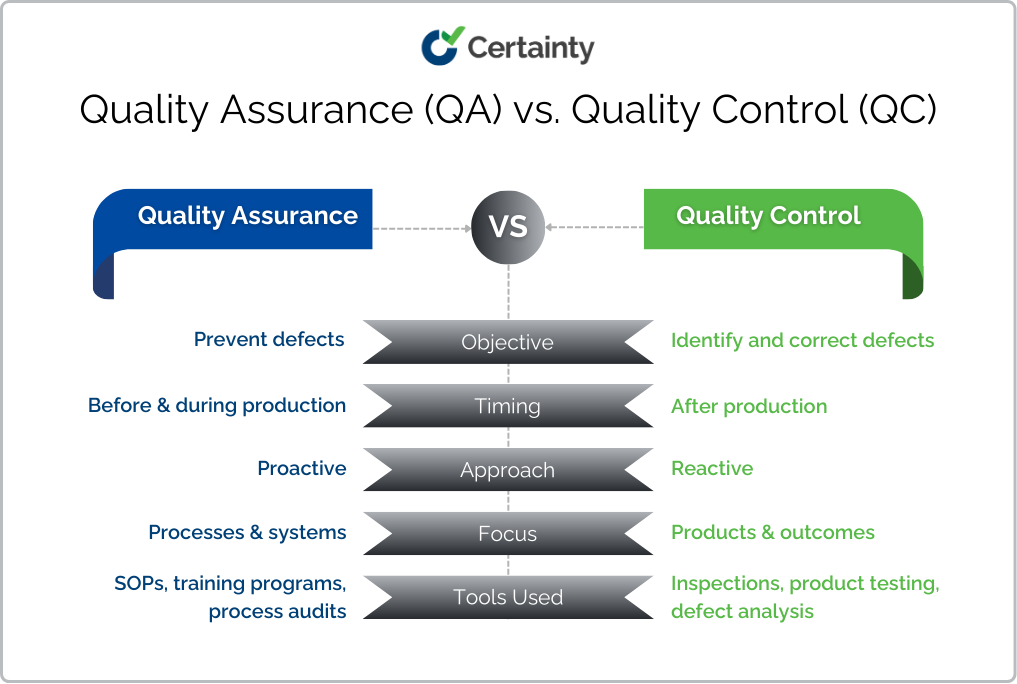
While QA lays the foundation for quality through prevention, QC provides the safety net by catching errors before they reach the customer. Both are critical for achieving consistent and reliable outcomes.
How QA and QC Work Together
QA and QC do serve different purposes – but they are most effective when used in tandem. A strong quality management system integrates the strengths of both approaches, creating a feedback loop that drives continuous improvement.
Consider an electronics manufacturing company. QA activities might involve designing a production process that minimizes stress on sensitive components, while the QC process involves testing finished devices to ensure durability under various conditions. The insights gained from QC can then inform QA processes, leading to further refinements and fewer defects over time.
Benefits of Effective QA and QC Strategies
Implementing robust QA and QC strategies offers numerous benefits, including cost savings, improved compliance, and enhanced customer satisfaction.
For example, a food manufacturer combining QA protocols (like HACCP plans) with rigorous QC methodologies (such as microbial testing) can prevent contamination while ensuring regulatory compliance. This dual approach reduces the risk of recalls, strengthens brand reputation, and fosters customer loyalty.
In addition to these tangible benefits, effective quality assurance and quality control activities also improve operational efficiency. By reducing defects, deviations, and rework, companies will save time, lower their production costs, and increase their overall return on investment.
Challenges in Implementing QA and QC (And How to Overcome Them)
Despite their importance, implementing QA and QC systems can be challenging. Common pitfalls include over-reliance on QC while neglecting QA, lack of employee training, and resistance to change.
One way to overcome these challenges is to leverage technology. Tools like Certainty Software can streamline inspections, audits, and reporting, making it easier to not only employ corrective actions but also maintain consistency across teams and locations. Additionally, fostering a culture of quality—where employees at all levels understand their role in maintaining standards—can significantly enhance the effectiveness of QA and QC systems.
Real-World Examples of QA and QC
Let’s look at how QA and QC play out in different industries:
- Pharmaceutical Manufacturing: QA involves creating protocols to maintain cleanroom conditions, while QC includes testing each batch of products for potency and purity.
- Automotive Manufacturing: QA focuses on supplier audits and process design, while QC inspects finished vehicles for defects like engine faults or paint imperfections.
- Food and Beverage Manufacturing: QA designs HACCP plans, and QC tests finished products for microbial contamination.
- Electronics Manufacturing: QA sets design standards, while QC conducts stress tests on devices to identify hardware failures.
How Certainty Software Helps You Manage QA and QC
Quality Assurance and Quality Control are complementary components of an effective quality management system. As you grow to understand their unique roles and integrate them effectively, your organization can achieve higher efficiency, stronger compliance, and greater customer satisfaction.
To optimize your quality management processes, explore how Certainty Software’s tools can streamline QA and QC activities, ensuring your organization stays ahead in today’s competitive market and meets global regulatory requirements.
Schedule your free call today with our team to learn more about how Certainty can support your quality management processes.
You might also be interested in:



