Environmental, social, and governance (ESG) frameworks are a priority for organizations. According to the 2022 EY US CEO survey, 82 percent of chief executives see ESG “as a value driver to their business over the next few years,” as both stakeholders and customers look for evidence that companies are doing their part to reduce negative environmental impacts, address social inequities and improve internal governance processes. To say having a high ESG score is important would be an understatement.
As more businesses make the move to ESG-driven operations, however, questions have emerged about how to effectively compare business ESG efforts — how do consumers or investors determine which organizations are doing ESG right, and which are falling behind?
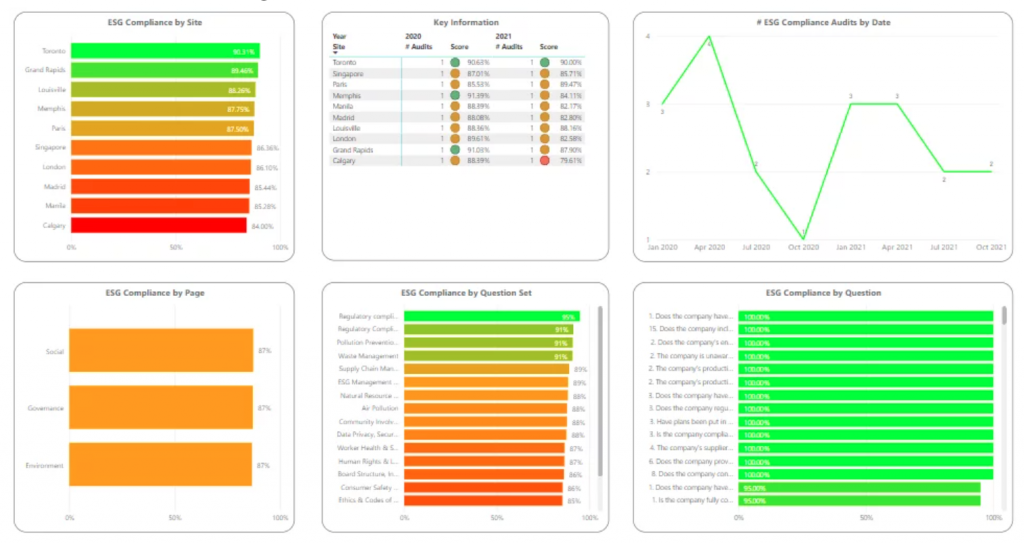
ESG scores have emerged as a way to help streamline this process by providing an overall assessment of environmental, social, and governance efforts.
What is an ESG Score?
An ESG score is a numerical measurement of how well business processes align with ESG expectations. This score provides a general sense of how sustainable an organization may be over time — for example, a low score in governance may indicate internal issues that could lead to challenges with staff retention, employee engagement, and effective management, while a low score in social impact may suggest issues with current business models or the management of human capital.
How is Your ESG Score Calculated?
ESG scores are calculated using publicly-available information to determine the efficacy of current policies in meeting ESG objectives. As a result, information not in the public domain won’t impact your score positively or negatively, but in both cases, this could pose a problem if ESG factors aren’t available.
Here’s why: These scores are largely a matter of perception — how companies are perceived to meet key goals. While metrics are evolving, standardization in this area is limited, meaning that there may be a disconnect between current operations and their actual impact on ESG outcomes.
To help bridge this gap, several measurement scales have been developed, including MSCI ESG Research, the Dow Jones Sustainability Index (DJSI), and the Bloomberg ESG Data Service. Consider the MSCI ESG Research index. MSCI ESG ratings evaluate companies across 37 different ESG issues and data points including carbon emissions, climate change vulnerability, renewable energy efforts, worker training, product safety, supply chains, accounting practice, and business ethics. Scores in each area are then combined to give an ESG rating from AAA – CCC; only 24 percent of companies achieve AAA annual reports. The DJSI and Bloomberg ESG Data Service, meanwhile, conduct rankings once per year and provide a score out of 100 with companies ranked against others in the same industry group.
Why Does it Matter to Your Business?
ESG scores matter to your business for several reasons.
First is perceived risk. A low ESG score means a higher risk that current company processes aren’t sustainable, in turn leading to hesitancy on the part of investors and shareholders — put simply, they equate ESG risks with financial risks and are less inclined to invest or support your organization.
Next is customer expectation. As noted by JD Supra, many customers now prefer to engage with brands that align with their personal values around environmental, social, and corporate governance issues. If businesses can’t demonstrate effective environmental or social policy via a solid ESG score, consumers may take their business elsewhere.

30+ Audit and inspection checklists free for download.
Increasing regulation is also driving ESG risk score adoption. In the EU, for example, the upcoming Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) will expand current reporting requirements, while in the United States the SEC established a task force to investigate ESG-related misconduct in 2021 and is now on track to develop new rules which will mandate ESG disclosures from any publicly-traded companies about climate change concerns and associated ESG risk ratings.
Achieving a Solid ESG Score
When it comes to scoring well on ESG initiatives, visibility is key. Consider the environmental and social aspects of ESG performance, which cover workplace environments, product safety, and operational risk. The more companies know about what’s happening on shop floors and production lines, the better they’re able to address critical issues and make positive changes. Here, tools such as robust checklists and auditing software can help pinpoint issues such as unsafe product handling or cluttered workspaces that could lead to staff injury and provide a framework for effective remediation complete with the documentation required to improve your overall ESG score.
Put simply, ESG evaluations matter. The better your score, the better your chances of capturing investor interest and keeping customers coming back. As a result, ESG investing is critical to driving good ESG practices, improving ESG reporting, and ensuring current practices align with evolving expectations.
You may also be interested in:
What Is Environment, Social & Governance (ESG) And Why Its Important



