Table of contents

Supply chain audits are a crucial part of keeping modern corporate processes transparent, compliant, and effective. However, these audits frequently turn out to be time- and resource-intensive, which has an effect on a company’s total productivity. Depending on the complexity of the business, the typical time to complete a supply chain audit might range from several weeks to several months. In this blog article, we’ll look at the importance of supply chain auditing, the typical reasons for audit delays, and—most importantly—the cutting-edge tactics and tools that can help organizations save crucial time when conducting audits.
Why Supply Chain Auditing Matters
Before getting into tactics for accelerating these audits, let’s take a look at the importance of supply chain auditing. Supply chain audits perform a number of vital tasks that include:
1. Supplier Quality Assurance
An essential part of verifying the caliber and dependability of suppliers is supply chain auditing. Audits support the maintenance of product quality and customer satisfaction by assessing supplier performance and compliance with quality standards. The danger of supply chain delays and interruptions brought on by poor supplier performance is reduced thanks to quality assurance.
2. Compliance Assurance
Supply chain audits assist companies in adhering to pertinent laws such as the recent GSCA, regulations, and industry standards such as SEDEX. In addition to being required by law, compliance offers a competitive advantage since it shows a dedication to ethics, quality, and safety. Businesses can benefit from audits by avoiding the expensive penalties, legal troubles, and reputational harm that could come from non-compliance.
3. Risk Mitigation
Businesses can recognize and control the numerous risks that could have an impact on their operations by conducting supply chain audits. These hazards can include things like labor disputes, supply breakdowns, natural disasters, and cyberattacks. Audits can assist companies in preventing or minimizing interruptions, losses, and damages as well as improving their operational resilience by identifying and addressing these risks early on.
4. Cost Efficiency
Supply chain audits reveal opportunities for improving the efficiency and effectiveness of the supply chain processes. These improvements can lead to significant cost savings, as well as increased productivity, quality, and customer satisfaction. Audits can help businesses optimize their inventory levels, reduce waste and errors, negotiate better contracts with suppliers, and streamline their logistics.
5. Brand Reputation
With the help of supply chain audits, businesses and their partners in the supply chain may develop a culture of openness and accountability. This can improve the company’s standing among its stakeholders, who increasingly appreciate ethical and sustainable business practices, such as clients, investors, regulators, and other stakeholders. Gaining and keeping the loyalty of clients, expanding market share, and boosting profitability are all possible with a good reputation for the business.
Challenges and Delays in Supply Chain Audits
It can be challenging to get around the supply chain audit landscape. These difficulties frequently cause delays in the audit process, which can negatively impact a company’s operational effectiveness and compliance. Let’s dig deeper into these difficulties:
Complexity of the Supply Chain
The sheer complexity of a company’s supply networks, which is particularly common in large corporations with broad, global supply chains, is one of the main obstacles that companies encounter during supply chain audits. These supply chains have several tiers of suppliers, each of which provides essential raw materials or support for the finished product. It can be a difficult and time-consuming procedure to locate and validate these tier 2 or tier 3 providers.
Take the automobile sector as an example. A single vehicle can contain thousands of components that are acquired from suppliers all over the world. It might be challenging to find your way through this complex web of suppliers and sub-suppliers to ensure compliance with legal requirements. Further complicating the audit process is the possibility that suppliers operate in numerous locations, each with their own regulatory framework and reporting framework.

Data Collection and Analysis Challenges
Many supply chain audits still rely on manual data collection, which has its own set of difficulties. Data collection from numerous sources throughout the supply chain is labor- and error-intensive. Inconsistencies and errors result from the process’ frequent use of paper records, spreadsheets, and various software programs.
Another difficult task is validating the accuracy of the data that has been gathered. It takes a lot of work to ensure that the data accurately reflects the supply chain’s current situation. Any inconsistencies or mistakes in the data can skew the audit findings and cause erroneous choices.
Lack of Transparency
Supply chain audits must be transparent, but not all vendors are forthcoming with the essential data. Some vendors can be reluctant to disclose data because of fear of disclosing confidential information or worry that they might not be following the rules themselves.
Suppliers can show resistance to divulging specifics regarding the place of origin and manufacturing procedures for their parts or goods. The audit process can be considerably hampered by this lack of openness, necessitating more time and effort on the part of auditors to convince or coerce suppliers to fully participate.
Inefficient Communication
For audits to proceed well, there must be effective communication between all of the supply chain’s stakeholders. Regrettably, poor communication techniques can cause significant delays. When auditors are waiting on responses or necessary data from suppliers, delays could happen. The auditing process may come to a complete stop if there is a slow flow of information.
Delays in getting responses, for instance, can impede the audit’s progress if auditors find a possible issue and seek clarification or additional data from a supplier. When working with suppliers in various time zones or countries, where response times may fluctuate, ineffective communication methods can make these delays much worse.
These difficulties and delays highlight the demand for novel strategies and tools to speed supply chain audits and guarantee that they are carried out successfully. In the sections that follow, we’ll look at several tactics and fixes that can aid companies in getting past these obstacles and squeezing more productivity out of the auditing process.
Strategies for Efficient Supply Chain Audits
It’s obvious that organizations must use cutting-edge tactics and technologies to speed up supply chain audits in light of the significant difficulties and potential delays. These techniques can improve your audit process’ overall effectiveness while also saving crucial time.
1. Leveraging Blockchain Technology for Transparency
A transparent and secure method of documenting supply chain transactions and events is provided by blockchain technology. Each transaction is safely recorded on a decentralized ledger, making it impenetrable to manipulation. Particularly in complex supply chains, this technology can dramatically cut down on the amount of time needed to track down suppliers and trace product origins. When blockchain technology is implemented in your supply chain audits you develop:
Immutable Records: The integrity of the audit trail is ensured by the fact that data recorded on the blockchain cannot be changed or removed.
Real-time Visibility: Stakeholders have access to real-time data on transactions and product movements, which eliminates the need for laborious data collecting.
Smart Contracts: By ensuring adherence to established rules and regulations, smart contracts make it feasible to automate audit processes.
Supplier Verification: Verification of the legitimacy and compliance of suppliers is made easier thanks to blockchain, which acts as a decentralized platform.
2. Applying AI Visibility and Optimization
Numerous uses of artificial intelligence (AI) are available that can greatly increase the effectiveness of supply chain audits:

Predictive analytics
AI-driven predictive analytics are essential for spotting possible supply chain problems before they get out of hand. AI systems can identify patterns and trends in previous data that might hint at potential threats or disruptions in the future. AI can examine data on supplier performance, traffic jams, or inventory levels, for example, to forecast potential bottlenecks or compliance difficulties. With these data at hand, auditors can prevent delays in the audit by taking proactive steps to mitigate risks.
Demand forecasting
AI is excellent at this task, which is essential for effective supply chain management. To produce highly accurate demand estimates, AI algorithms can examine previous sales data, market trends, and other pertinent aspects. Businesses may optimize inventory levels by ensuring that products are available when needed without having extra stock, which can cause inefficiencies and audit delays when they have accurate demand projections in hand.
Supply Chain Visibility
Real-time visibility into supply chain processes is provided through AI-powered technologies. These technologies gather and analyze information from numerous sources, providing a thorough understanding of the complete supply chain. The status of shipments, inventory levels, and production procedures may all be tracked in real-time by auditors. AI systems can generate alerts when discrepancies or difficulties occur, allowing auditors to resolve concerns quickly and stop them from delaying audits.
Automation
A basic competency of AI, automation is essential to streamlining the auditing process. Automation technologies powered by AI can easily collect and arrange data from numerous sources, minimizing the need for manual data entry and the possibility of human error. Instead of becoming mired down in data collection, auditors can devote more time to value-added tasks like analysis and decision-making, thus accelerating the audit timeframe.
Data-driven insights
The data processing abilities of AI provide auditors with useful information. AI can find trends and abnormalities in supplier behavior, production efficiency, and compliance adherence by analyzing massive datasets. AI, for instance, may identify suppliers with recurrent quality problems, track down lead time fluctuations, and identify high-risk non-compliance zones. These insights direct auditors to concentrate their attention on the most important areas, improving audit efficiency and lowering the possibility of audit delays.
Risk assessment
The capacity of AI to evaluate risks is priceless. AI can pinpoint high-risk areas in the supply chain by examining data on supplier stability, geopolitical variables, and market conditions. These locations can include crucial suppliers situated in disaster-prone areas or suppliers who are experiencing financial difficulties. With this knowledge, auditors can prioritize high-risk areas and devote more time and attention to them in order to reduce the likelihood of delays brought on by disruptions.
3. Implementing Gamification Techniques
Supply chain audits benefit from gamification’s motivational and engagement-boosting effects for a number of reasons.
Incentives for Compliance
Giving suppliers incentives for adhering to audit standards is one of the key components of gamification. These inducements may come in the shape of material benefits, acceptance within the supplier network, or even preferred supplier status. Businesses can encourage suppliers to actively engage in audits and fulfill deadlines by providing incentives for compliance, which will ultimately result in fewer delays because of audits.
Real-time Feedback
Platforms that use gamification offer an interactive setting where suppliers and auditors can communicate in real-time. Suppliers can receive quick feedback from auditors, who can also direct them about compliance and transparency requirements during the audit process. This continuous feedback loop makes sure that any problems or discrepancies are resolved right away, preventing them from slowing down the audit process.
Competition
Gamification fosters a spirit of cordial competition among vendors. Businesses might develop scorecards or leaderboards that highlight their top suppliers. The desire to surpass their competitors drives suppliers to actively participate in the audit process. As a result, they frequently go above and beyond compliance regulations. The amount of competition greatly lowers audit-related delays.
Training and Education
Suppliers can learn a lot from gamified modules, which can help them comprehend audit procedures and standards. These modules could contain amusing and instructive interactive games, tests, or simulations that involve providers. Businesses may guarantee that their suppliers are ready for audits by offering them clear and interesting resources. This proactive strategy reduces the amount of time that non-compliance or misinterpretations of audit expectations cause delays.
4. Automation with Certainty Software
A complete solution from Certainty Software automates the supply chain audit’s data collecting, processing, and reporting procedures. The main benefits are as follows:
Streamlined Data Collection
Through user-friendly interfaces and mobile applications, Certainty Software makes data collection easier. Data entry by auditors and suppliers is simple, which eliminates the need for laborious manual data entry. The audit process is expedited by optimizing the data collection procedure, which also reduces the possibility of human error-related delays.
Real-time Analytics
Real-time reporting and analytics capabilities are offered by the platform. Auditors have rapid access to current data, enabling them to make informed decisions and respond quickly when problems develop. With this real-time information, audit schedules are not jeopardized by sluggish data analysis.
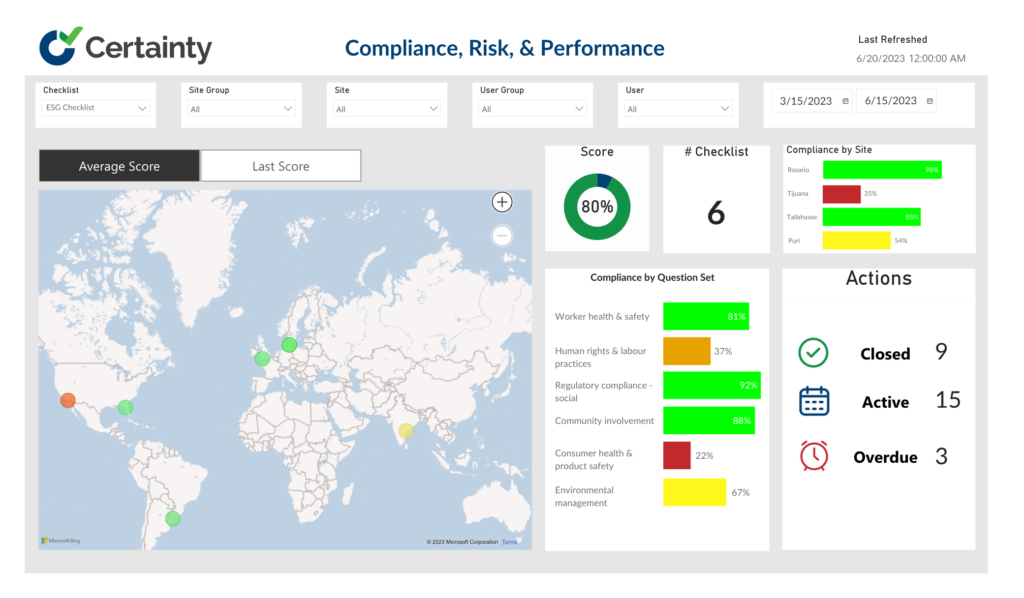
Customizable Templates
Businesses can customize audit templates using Certainty Software to meet their unique needs. This adaptability makes sure that audits properly match the requirements and standards of the firm. Auditors can optimize the audit process and reduce potential delays brought on by outmoded protocols by adjusting audit templates to changing compliance criteria.
If you’re interested in digitizing and improving your supply chain audits, book a call here to discover how Certainty Software can boost your supply chain audit success.




