According to one study, businesses that implemented the ISO 9000-based quality standards found an 18% increase in client satisfaction and a 15% cost reduction. ISO 9001 is an internationally recognized Quality Management System (QMS) criteria program. This program guides businesses of any size to maintain or find improvements in their quality management system and processes. The ISO approach and ISO 9001 audit is based on the Deming Cycle of continuous improvement – plan, do, check, act.
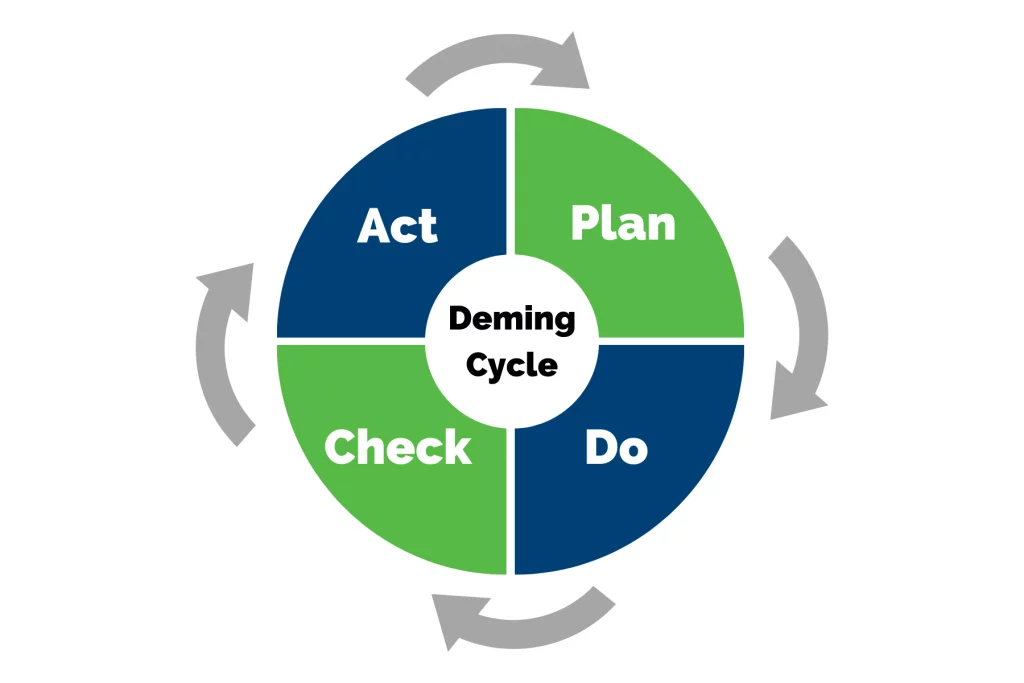
To either become certified or to maintain ISO standards once certified, auditing both externally and internally are necessary action. The iso 9001 audit aims to address 3 key areas of your Quality Management System:
- Verify your QMS aligns with the ISO 9001 audit standards.
- Identify areas of concern within your quality system.
- Develop corrective actions and opportunities for improvement.
What are the 3 Types of ISO 9001 Audits?
An ISO 9001 audit can be divided into either general internal or external auditing. Internal auditing is conducted within the business and holds accountability to meet the standards created by ISO. External audits are scheduled and completed by auditors external to the business. External auditors offer precision knowledge of ISO standards and opportunities for new perspectives on your business’s Quality Management Systems.
There are three options that businesses have when choosing how to conduct their iso 9001 audit:
Self-auditing does not necessarily mean an audit is completed by management or employees. Rather, it also includes reflecting on the feedback that a business’s customers have provided, or a surveillance audit.
On-site audits are pre-scheduled and typically take at least a full business day to conduct. Auditing completion time varies on factors such as business size, QMS complexity within the business, and other factors. The external iso 9001 audit frequency varies but is typically conducted on an annual basis.
Remote audits can be completed through web meetings, phone calls, and electronic document transfers. These are less effective than on-site auditing and therefore less common.
What is the Internal ISO 9001 Audit Process?
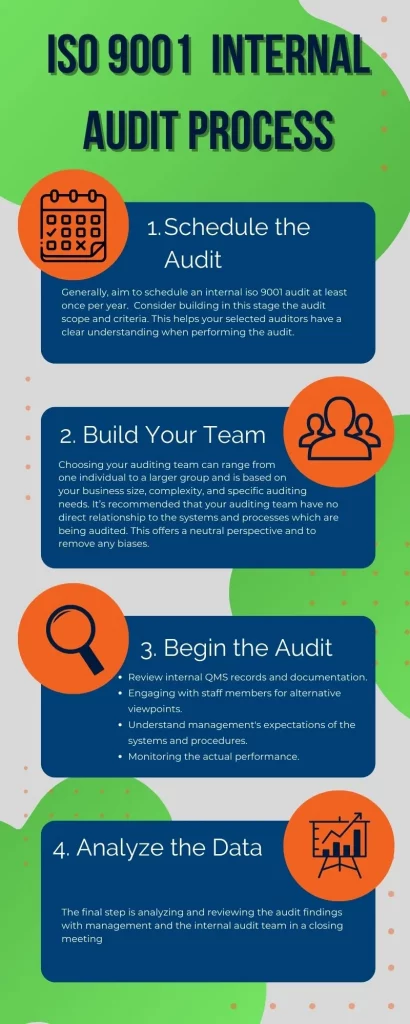
The iso 9001 internal audit process is a self-check opportunity to ensure your QMS and processes meet the ISO standards. For a more effective internal iso 9001 audit, it is recommended to follow these four steps:
1. Schedule the Audit
Generally, aim to schedule an internal ISO 9001 audit at least once per year. Of course, this varies based on the complexity of your quality management systems and may require more frequent internal auditing. In addition to building the audit schedule, consider building the audit scope and criteria. This helps your selected auditors have a clear understanding when performing the audit.
2. Construct the Audit Team
Choosing your auditing team can range from one individual to a larger group and is based on your business size, complexity, and specific auditing needs. It’s recommended that your auditing team have no direct relationship to the systems and processes that are being audited. This offers a neutral perspective and removes any biases.
Selecting a neutral auditing team with no direct involvement in your QMS also creates a challenge for the auditing process. The lack of quality system experience by the internal auditor(s) could result in key audit findings being missed and a failure to meet the requirements of ISO 9001 unless clear auditing directions are given.
To avoid setbacks from this challenge, we recommend using a quality assurance checklist that covers all necessary auditing components and reduces missed observations by your auditing team. Additionally, we recommend conducting a series of internal auditor training to familiarize your internal auditors with the procedures and tools required for a well-performed audit.
3. Begin the ISO 9001 Audit
Now that you’ve assembled your ISO internal audit team, and the auditors have been briefed thoroughly at your opening meeting on the auditing process and objectives, the actual auditing process may begin. For the ISO internal audit to be a success, we recommend ensuring the following 4 tasks are audited:
- Observing internal records and documentation related to QMS.
- Engaging with staff members for alternative viewpoints on performance.
- Developing an understanding of management expectations of the systems and procedures.
- Monitoring the actual performance of the systems and procedures.
Having to examine many different systems and procedures associated with the internal ISO 9001 audit can create hurdles for your auditing team. More specifically, if they aren’t given the supportive audit tools to enter observations in real time, delays in audit completion are more likely to occur. Also, tools for streamlined data prevent having to recall and input observations at a later time, improving your audit result accuracy, and ultimately meeting the standards set by ISO.
4. Analyze the Data
The final step is analyzing and reviewing the audit findings with management and the internal audit team in a closing meeting.
A common barrier to success at this stage is being unable to organize the data into clear and actionable reports quickly. Centralizing the audit data to output meaningful information for management review supports a continuous improvement culture in addition to conforming to the QMS standards set out by ISO. We recommend finding a software solution that is capable of centralizing your internal ISO 9001 audit data in real-time, and into simple to-analyze reports – making your next ISO internal audit a huge success.
Tips to Prepare for an External ISO 9001 Audit
Perform Internal Audits
Internally verify that you’re QMS is meeting the ISO certification standards by performing internal audits and check-ins. Typically, internal audit programs are the first step to recognizing when quality standard processes and/or systems are failing to meet ISO standards.

30+ Audit and inspection checklists free for download.
Verify Documentation
As the auditee, any relevant documentation involved in your quality management system should be approved and up-to-date. Suggested documents to verify include:
- Flowcharts
- Quality objectives
- Instruction manuals
- Policies
- Records
Train Employees
Employees should be aware and trained for the ISO 9001 audit process and what they can expect during the audit procedure – such as employee interviews. Additionally, training on organizational quality procedures and objectives should be an ongoing process regardless of upcoming ISO 9001 external audits.
Maintain a Culture of Continuous Improvement
When an organization embodies a continuous improvement culture, it translates into better performance for both the ISO certification audit and the ISO standard verification audit. This culture welcomes employee engagement and input into quality systems and provides new perspectives that may have been unforeseen by senior management.
You may also be interested in:
What Are Quality Assurance Inspections And Why They Matter
Improving Operational Quality: The Role Of Qualitative Risk Assessment



